

The values of the trigonometric functions can also be represented by the lengths of the line segments in a coordinate plane with a unit circle as show in the diagram below. Thus, on the unit circle, cosine and sine can be defined as:Ĭosecant, secant, and cotangent are the reciprocals of sine, cosine, and tangent respectively, and are defined as: The point at which the terminal side of the angle intersects the unit circle has an x-value of cos(θ) and y-value of sin(θ). The terminal side of the angle is the hypotenuse of the right triangle and is the radius of the unit circle. θ is the angle formed between the initial side of an angle along the x-axis and the terminal side of the angle formed by rotating the ray either clockwise or counterclockwise. In such a triangle, the hypotenuse is the radius of the unit circle, or 1. Given a point (x, y) on the unit circle, we can form a right triangle, as shown in the figure.
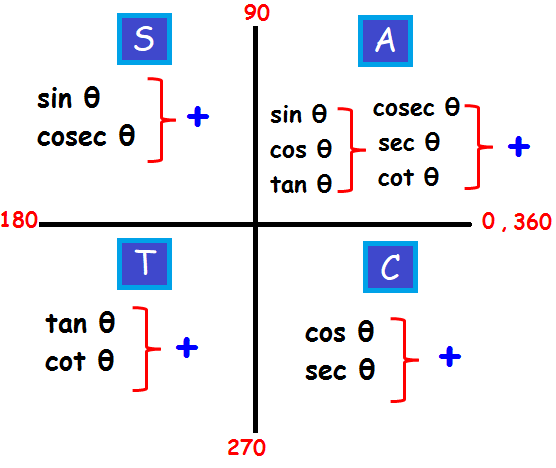
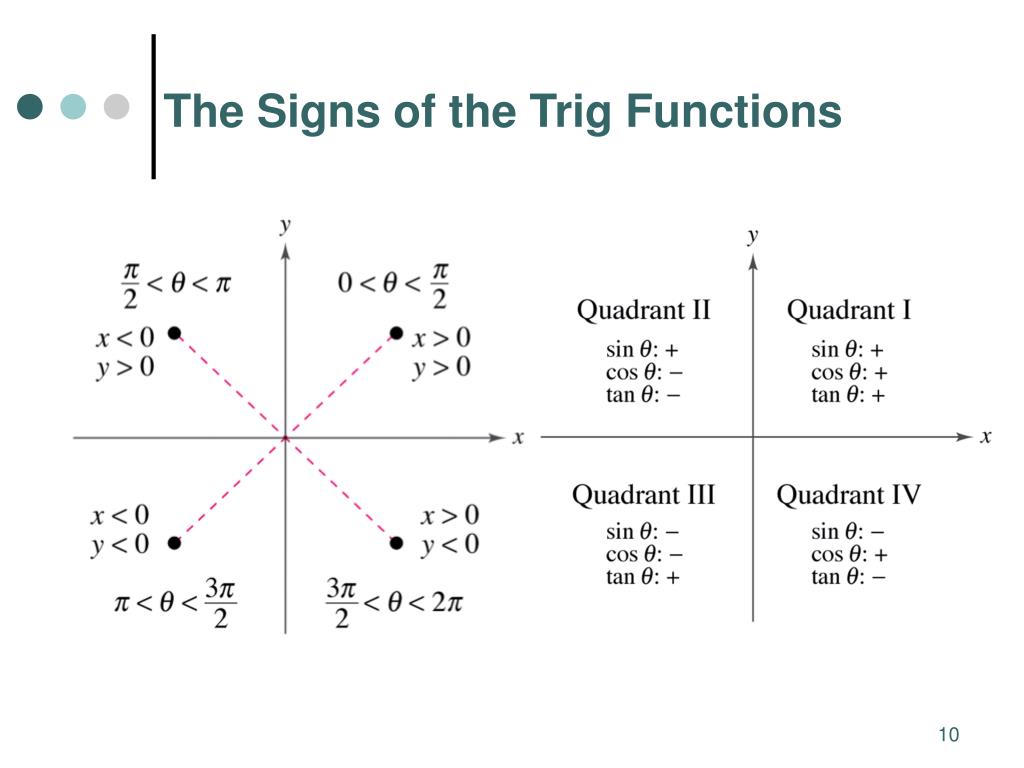
Using the unit circle definitions allows us to extend the domain of trigonometric functions to all real numbers. The right triangle definition of trigonometric functions allows for angles between 0° and 90° (0 and in radians). A unit circle is a circle of radius 1 centered at the origin. Trigonometric functions can also be defined as coordinate values on a unit circle. These functions are often written in their abbreviated forms. The following are the definitions of the trigonometric functions. Consider an angle θ as one angle in a right triangle. The output of a trigonometric function is a ratio of the lengths of two sides of a right triangle. The right-angled triangle definition of trigonometric functions is most often how they are introduced, followed by their definitions in terms of the unit circle. There are two main ways in which trigonometric functions are typically discussed: in terms of right triangles and in terms of the unit circle. Refer to the reference angles section below for more detail as well as a table of the signs of the six trigonometric functions in each quadrant. We can find the values of the other trigonometric functions in the same way. Similarly, since the value for cos(330°) in quadrant IV is positive, it has the same value as cos(30°). Since the values of cosine in quadrants II and III are negative, the value for cosine for the corresponding angles in quadrants II and III (150° and 210°) is. For example, the value of cosine for 30° or in the first quadrant is. We know that cosec x is not defined at integer multiples of pi, so the cosecant function graph has a discontinuity at points nπ, where n is an integer.Although the table does not include the multiples of each angle in each quadrant, we can use the table to find the values of the other angles the values are the same for each corresponding angle, taking the sign of the respective quadrant into consideration.

Is Cosecant Function Graph Continuous?Ĭosecant Graph is not continuous as it has vertical asymptotes at points where cosecant function is not defined. Hence, cosecant is the reciprocal of the sine function. Also, the product of these two functions at an angle is always equal to one. We know that sin x is the ratio of perpendicular and Hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle and Cosecant is the ratio of perpendicular and Hypotenuse, so cosecant is the reciprocal of sine. The values of the cosecant function repeat after every 2π radians, so the period of cosec x is equal to 2π radians (360 degrees). It is written as sin x = 1/csc x What is the Period of Cosecant? The reciprocal of the cosecant function is the sine function. The inverse of sin is called inverse sine or arcsin. It is the reciprocal of the sine function. Secant is the ratio of hypotenuse and adjacent side whereas cosecant is the ratio of the Hypotenuse and Opposite Side. Secant function is the reciprocal of the cosine function and the Cosecant function is the reciprocal of the sine function. What is the Difference between Secant and Cosecant? We can also find the cosecant of angle using trigonometric identities.
The cosecant of an angle is equal to the ratio of the hypotenuse and opposite side of the angle in a right-angled triangle. csc x = Hypotenuse/Perpendicular OR Hypotenuse/Opposite Side.The cosecant function formula can be written in two different ways: It is the reciprocal of the sine function and hence, is equal to the ratio of Hypotenuse and Perpendicular of a right-angled triangle. The cosecant function is one of the important six trigonometric functions. FAQs on Cosecant What is Cosecant Function in Trigonometry?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
